Whitepaper
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and type
Newsroom
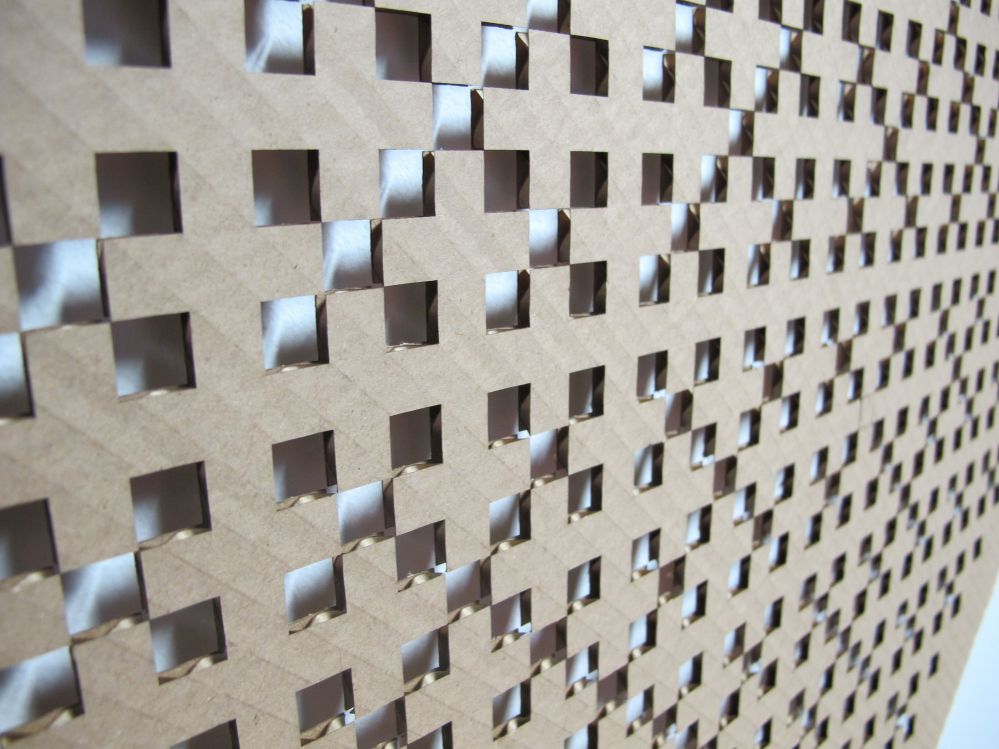
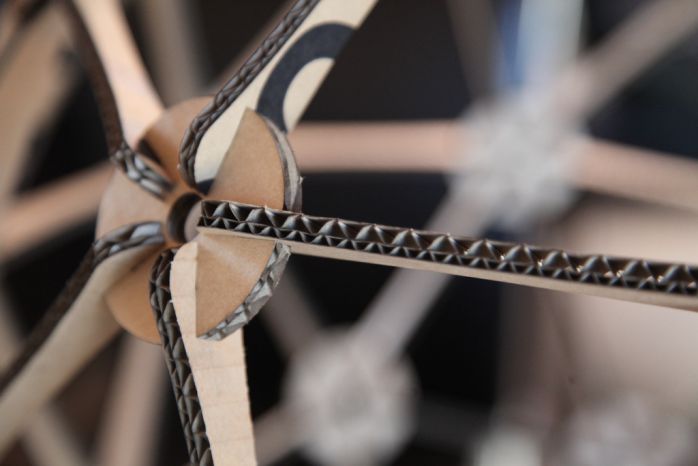
Laser cutting corrugated cardboard
Corrugated cardboard, also known as corrugated fiberbord or simply cardboard, is the most widely used packaging material. Its low production
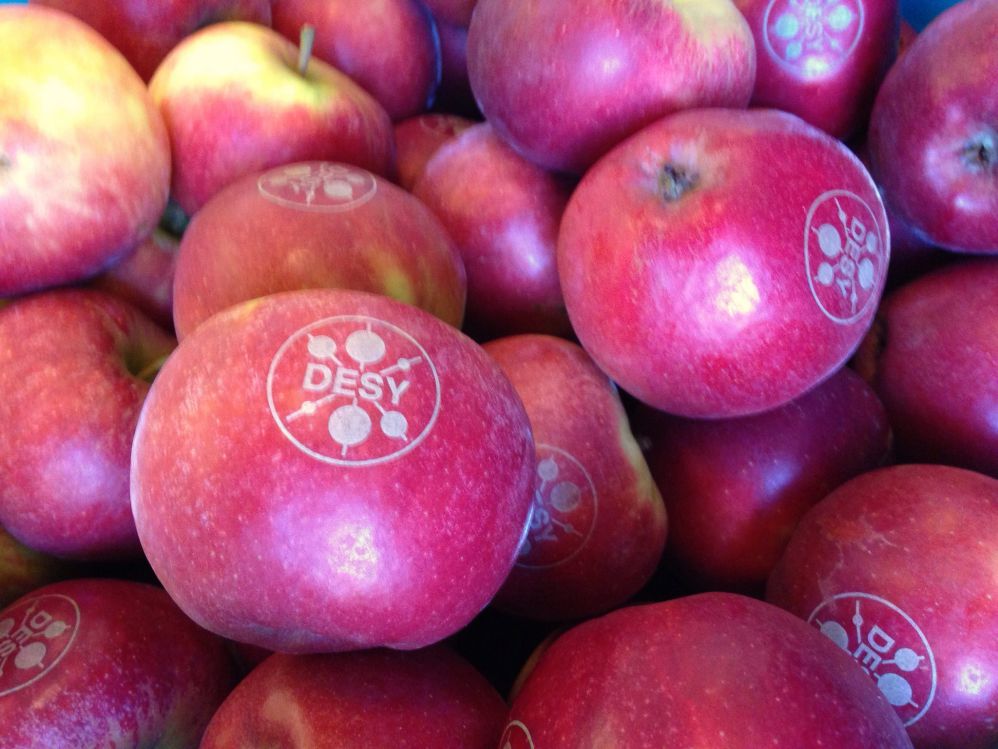

Laser labeling of food with laser marking
What if producers and distributors of fruit and vegetables stop using sticky labels? It’s not phantasy but reality: with laser
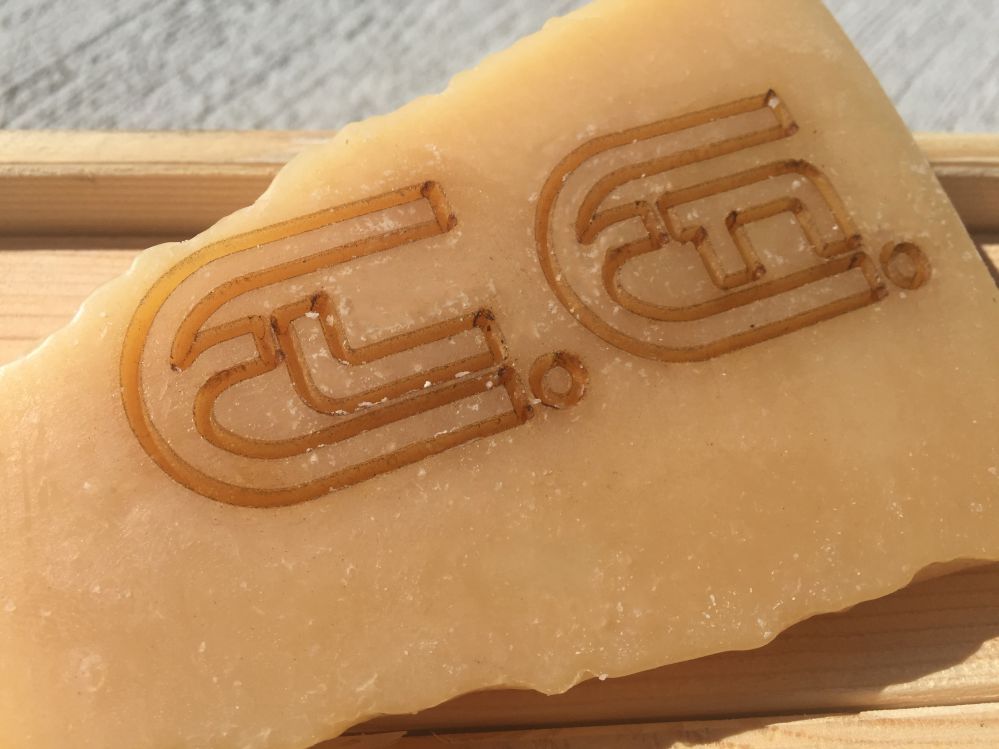

Laser Marking For Cheese and Ham
Laser labeling of food is a recent innovation that makes it possible to reduce production waste by replacing traditional food

Laser micro-perforation of plastic bags for fresh products
One of the characteristics of CO2 lasers is that it allows you to carry out processes which were impossible to

What materials can be cut by a CO2 laser?
Wood, paper, cardboard, plastic, PMMA. And also rubber, leather, metals, and ceramics: CO2 lasers can cut a great number of
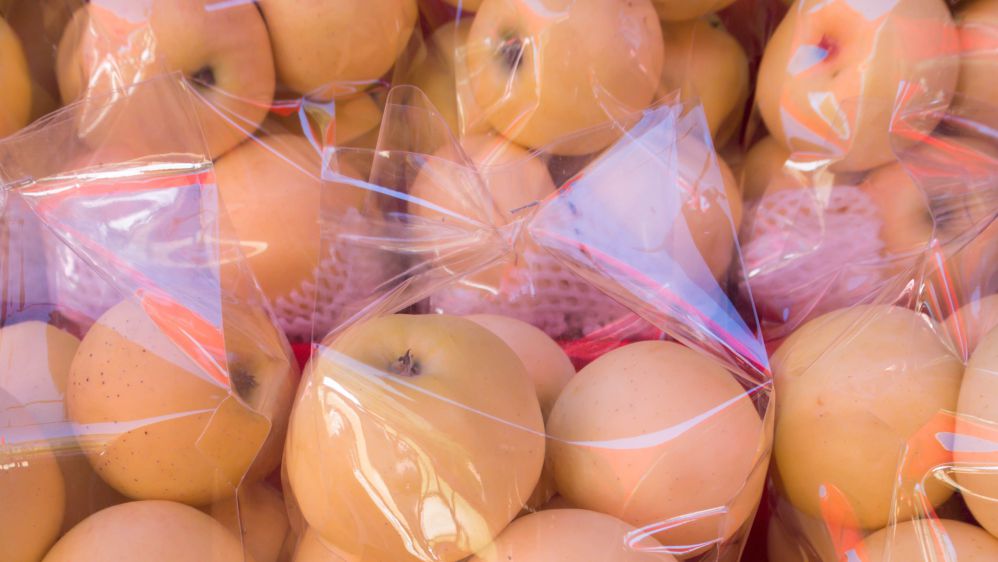

Hermetic laser sealing of plastic food bags: what it is, how it works, and the advantages
Let’s continue our journey of discovery of the different CO2 laser applications for the packaging industry. In the past articles,
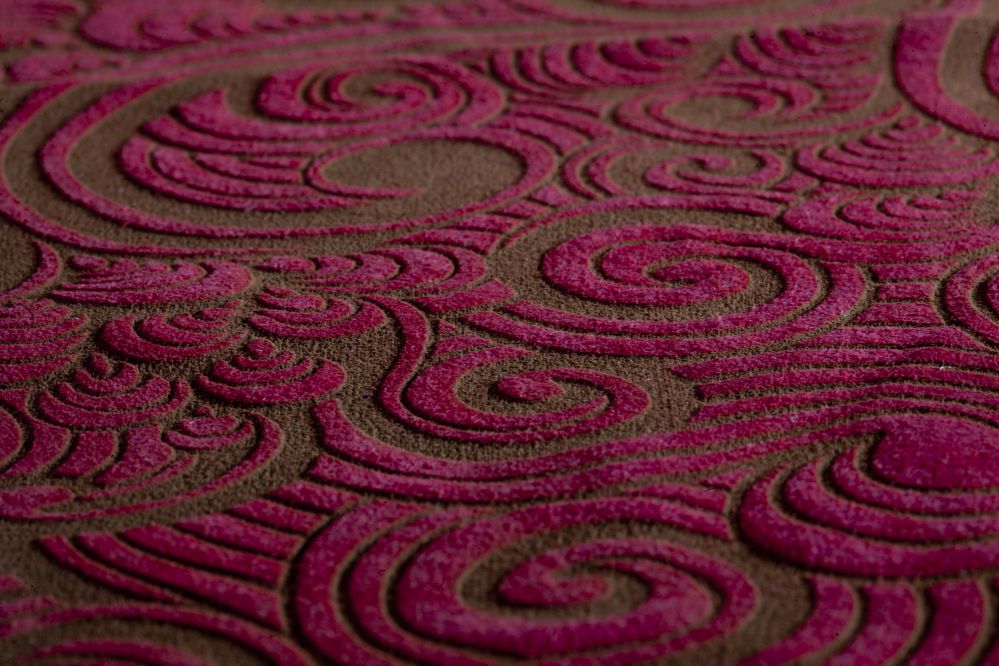

Laser Engraving Fashion Design: a sustainable application
The clothing industry is the second biggest polluting industry, being just behind the petrol industry. To give you an idea

Laser Die Cutting vs. Rotary Die Cutting: an innovative technique for the packaging industry
The introduction of lasers in industrial processes has been a small revolution: the effectiveness and versatility of this technology has
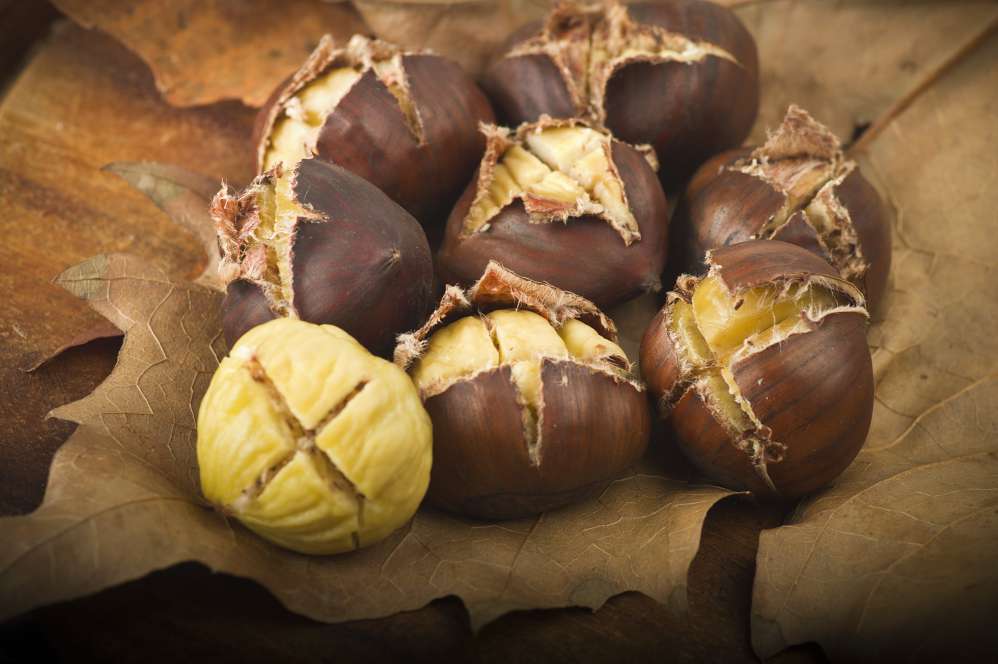

Peeling fruit with laser technology
Peeling fruit and vegetables using laser technology? It is possibile. And it is only one of the many applications of



