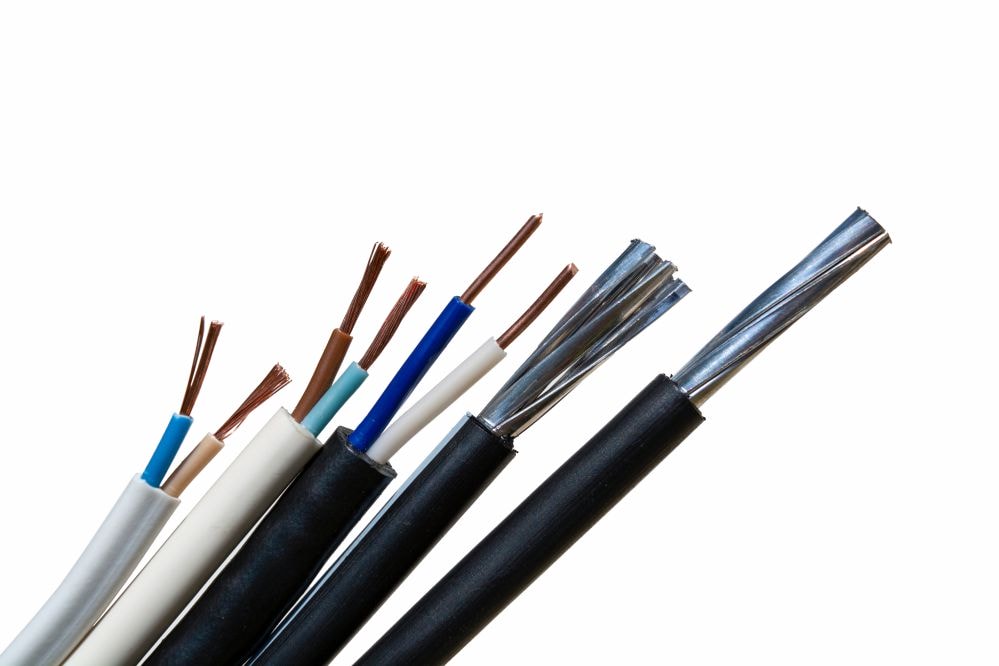
Laser wire stripping is the process of removing all or part of the insulating material that covers electrical cables. In other words, it is the process used to uncover the metal core of the cables. It is typically done at the cable’s ends to make connections possible, but it can also be done in various ways along the cable.
Laser stripping’s main feature is that the laser selectively intervenes on the insulating material without affecting the cable’s metal core. This is a significant advantage over traditional stripping techniques. The high quality and precision of the laser striping process has made it a widely used technique in high-tech sectors.
Not surprisingly, the idea of ​​using lasers to remove the insulating layer of electrical cables was born in the aerospace sector. In the 1970s, NASA needed to find a solution to strip the thin Space Shuttle cables. The stripping tools used at the time did not guarantee the quality and precision necessary for an application of that type.
Traditional wire stripping methods and their drawbacks
The first is the mechanical method, which is the most widespread. In this process, blades are used to cut the electrical cables’ sheathing.
This method has many drawbacks:
- to achieve accurate results, the process becomes extremely slow
- each type of cable requires a dedicated tool
- the tools require maintenance to remain effective
The risk of damage, for example notching the cable, is one of the main risks of this technique. To solve this problem, manufacturers have produced oversized cables, so that any loss of metal would not reduce the functionality of the cable.
While this may be a solution for low-tech industries, oversizing cables is not a suitable solution for others.
In the aerospace sector, for example, weight containment is essential. Cables are designed to be very thin so that they weigh as little as possible. This means that any damage to the cable could cause it to malfunction and lead to accidents.
In addition to the mechanical method, peeling can be performed with a chemical or a thermal process.
The chemical process uses corrosive substances such as sulfuric acid to dissolve the cable coating and expose the conductive material. The disadvantage of this technique is that it is not easily controlled and is also polluting.
The thermal process uses a heat source to remove the coating. This method, however, can leave residual coating material on the metal core which would therefore have to be subjected to further processing.
Laser stripping overcomes all the previously mentioned drawbacks. It is therefore not surprising that it has established itself as the method of choice for high-tech applications.
Why laser stripping works
In most cases, the material that coats electrical cables is some kind of plastic polymer while the internal core is made of metal, very often copper. Laser technology has the ability to select only the coating’s polymers without modifying the conductor in any way.
This behaviour can be explained by the way laser radiation interacts differently with different materials.
CO2 laser emits radiation at a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers, that is, in the far infrared [far-IR] region. Polymers absorb this radiation very well while copper reflects it almost completely, without undergoing alterations.
The advantages of laser stripping
Laser stripping offers several advantages over traditional methods:
- flexibility: it is effective on almost all polymeric materials with which electrical cables are coated
- precision: it is a non-contact process, which makes it able to work on very tight tolerances and to carry out processes that would be impossible with traditional methods
- effectiveness: since laser is reflected by most metals, the process ends with the removal of the polymer without requiring any further processing
What are the different types of laser stripping
In laser stripping, the laser can perform 3 basic operations:
- laser cross cutting: the cut is carried out transversely to the cable in order to allow the removal of excess material
- laser slitting: the cut is made lengthwise. Typically this process is performed when a longer portion of cable needs to be removed and is used in conjunction with the cross cut
- laser ablation: the laser passes over the surface several times until the coating is completely eliminated. This technique is mainly used when the conductive material is immersed in the coating (otherwise known as bonded wire).
Alongside these basic operations, laser technology makes it possible to perform advanced processes such as the partial and targeted removal of the coating with the creation of windows or the removal following certain patterns. All these applications can’t be done with traditional mechanical methods.
As is often the case with lasers, the possibilities are endless.
How a laser stripping system is made
A laser cable stripping system can be implemented in various ways and with various technologies.
The most effective is certainly galvo-scanning. In this application, a scanning head is used to move the laser beam and then focus it on the work surface.
The whole system is controlled by a computer which coordinates the operation of the CO2 laser source allowing the laser to follow the pre-defined cutting path.
Implement your own laser wire stripping
Laser cable stripping lends itself to many applications. It is ideal for high-tech sectors that require great precision during the processing phase. One of the applications, for instance, is magnet wire stripping with laser.
Don’t hesitate to contact us. Our staff would be happy to advise you on the best laser solution for your needs.